Harness the Power of Data with Improved Data Collection
Agencies have a wealth of data at their fingertips from both internal and external sources. They use it to support critical reporting, decision-making, and overall mission-success. Yet, agencies may struggle to leverage their data for meaningful insights due to challenges with data collection. These challenges include a lack of governance processes, fragmented, manual, or inconsistent processes, and siloed or ineffective data management systems. These may contribute to data quality issues, including incomplete, inaccurate, or unreliable data. The good news is that agencies can overcome some of these challenges by methodically improving data collection.
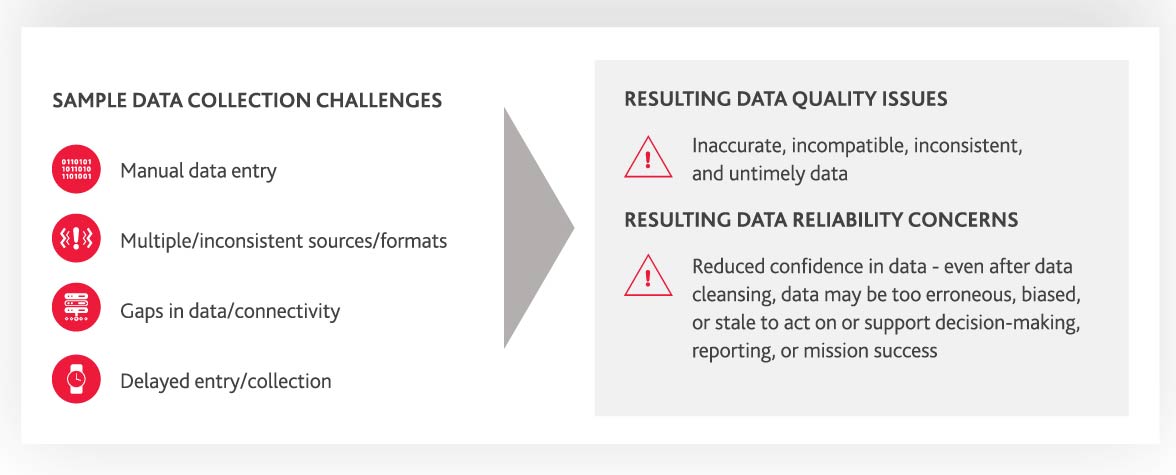
As shown in Figure 1 below, failing to address these challenges can have detrimental ramifications on compliance, financial and operational performance, strategic objectives, and the agency’s ability to accomplish its mission.
Figure 1: Ineffective Data Collection Undermines Mission Success
Improved Data Collection Case Study
Learn how BDO improved data collection and utilized extensive data analysis to support mission success and achieve 100% compliance with reporting requirements related to Environmental & Disposal Liabilities Cost-to-Complete estimates.
How to Improve Data Collection
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to data collection, but agencies can implement the three-phased approach described below to help them consider improvements that best align with their objectives and needs.
1. Plan Phase: Current State Assessment
Agencies should begin with an upfront assessment of the current state of data collection. This will help to evaluate the organization’s data maturity and identify meaningful improvement opportunities. The assessment should entail gathering and reviewing documentation and interviewing stakeholders in relevant governance bodies, offices, or departments.
The current state assessment should focus on three specific aspects of data collection that are essential to all agencies: data governance, data collection processes, and data management systems. Figure 2 below provides definitions of these components, and sample considerations for assessments. Upon completing the assessment, a summary of specific and actionable improvement opportunities should be documented.
Figure 2: Essential Data Collection Components
Data Governance The structure for defining authorities, requirements, and oversight of data. | Data Collection Processes The processes for collecting information from various sources so it can be compiled, analyzed, reported, or used to support decision-making. | Data Management Systems The systems used to collect, store, and analyze data across the organization. |
Sample Considerations For Assessments | ||
|
|
|
2. Evaluate Phase: Review and Prioritize Improvements
To foster collaboration, transparency, and a shared vision for the agency’s future state, the project leader should share improvement opportunities with relevant stakeholders so they can discuss and prioritize them. When defining goals for data improvements, consider these factors:
- What the improvement aims to accomplish (e.g., improved delivery of mission-critical services, improved compliance, and better decision-making)
- How the improvement addresses the root cause of ineffective or inefficient matters
- How improvements should be measured (to define what success looks like)
- Which stakeholders should be responsible for overseeing improvements
- Whether there are relevant dependencies for implementing improvements
Stakeholders should also weigh additional factors, such as short- and long-term benefits, cost savings, time efficiencies, and return on investment when selecting and prioritizing improvements. After selecting areas of improvement, it is important to formalize and document decisions and any implementation plans.
Figure 3: Examples of Value-Added Data Collection Improvements
| Improvements | Benefits |
| Establish governance | Defining roles and responsibilities across relevant stakeholders can clarify accountabilities and guide the efforts of the parties involved. |
| Automate data collection processes | Implementing an automated data collection system can streamline data collection processes and reduce the risk of errors, leading to improved data quality and reliability. |
| Improve data validation procedures | Implementing more rigorous data validation procedures, such as using data validation rules for data ingestion or performing regular data audits, can improve the accuracy of the data collected. |
| Secure data | Enhancing data protections can prevent unauthorized use or manipulation. For example, organizations can implement controls for credentialed users to ensure that access rights are permitted in accordance with laws, regulations, and policies. |
| Integrate systems | Integrating the data collection system with other systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, can provide a more comprehensive view of data across multiple stakeholders. |
| Provide training and support | Promoting data literacy training (particularly among project managers and contracting officers’ representatives) can help the team to understand the importance of data quality and reliability and how to maintain it. |
| Leverage data analytics tools | Implementing data analytics tools, such as dashboards, reports, and trackers, can make data analysis faster and more effective, leading to better insights and decision making. |
3. Execute Phase: Implementing and Monitoring Improvements
As with any rollout, change management is key. It is critical to communicate early and often about planned improvements, including explaining the “why” of any changes to help gain stakeholder buy-in and manage expectations about the upcoming changes. In addition to designing enhanced or new governance, processes, or data management systems, it is important to deliver timely and practical trainings to relevant stakeholders to help them get comfortable with updates. This includes developing training schedules, managing pilot programs, as appropriate, and providing easy-to-use reference materials or resources for ongoing support.
Proper monitoring is critical to make sure that improvements progress appropriately. This may include performing recurring touchpoints with parties responsible for overseeing improvements, collecting evidence of completed activities, verifying, and validating the progress, and monitoring milestones to confirm timely execution.
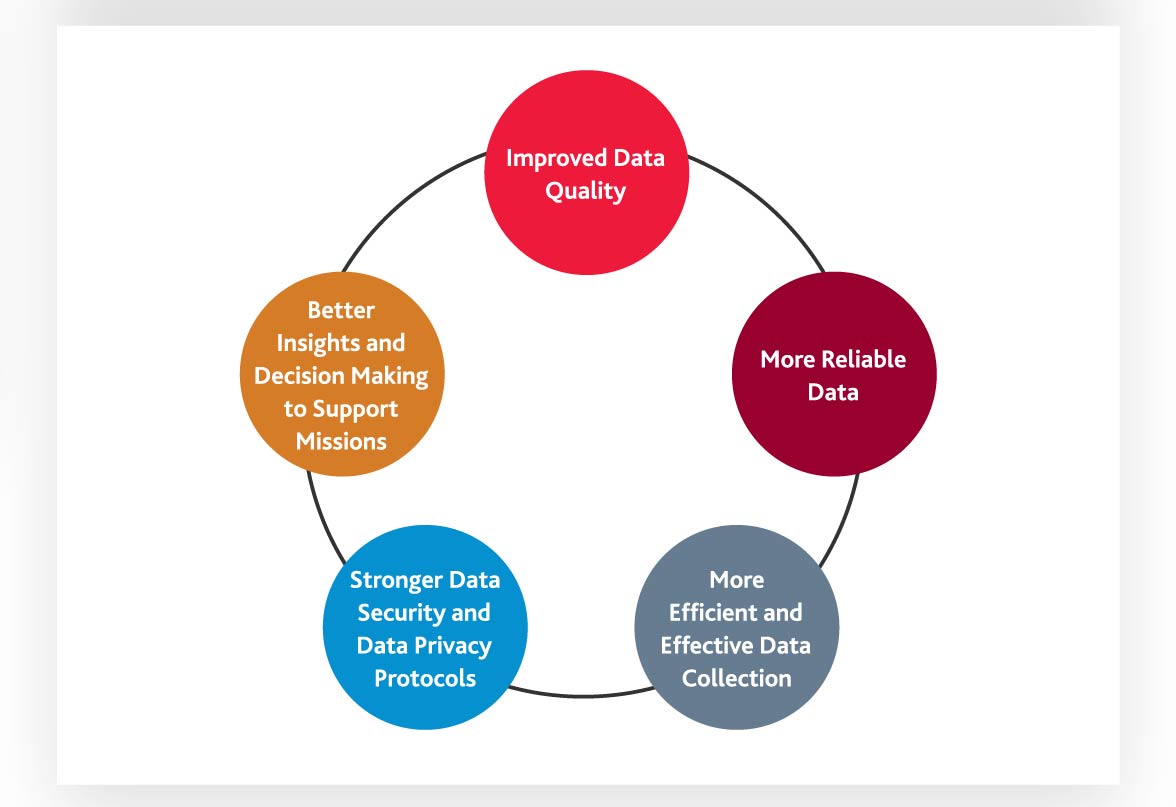
Proper monitoring can also help to identify further improvement opportunities, and continually enhancing data collection processes to support agencies in accomplishing their missions more effectively and efficiently.
Figure 4: Benefits of Continually Improving Data Collection
BDO Government and Public Sector
BDO’s Government & Public Sector practice delivers innovative and sustainable services to address your most complex challenges. We can help in the areas of data management, data analytics, data modeling,
Robotic Process Automation (RPA), app development, and digital transformations. Our thought leaders and seasoned professionals bring a wealth of experience that enables us to tailor our approach and adapt quickly to your needs.
SHARE