Key Points:
- The importance of data governance cannot be overstated. With advanced technology and artificial intelligence relying on accurate, structured data to function effectively, strong controls around the way companies store and organize their data have become essential.
- A solid data foundation provides a platform that can help organizations conduct better risk assessments, enable AI-powered tools, and create a smooth audit experience.
The importance of data governance cannot be overstated. With advanced technology and artificial intelligence relying on accurate, structured data to function effectively, strong controls around the way companies store and organize their data have become essential. Advances in audit tools also necessitate a solid data foundation to create an efficient experience throughout the audit process.
Despite this, nearly 70% of respondents to BDO’s 2024 Audit Innovation Survey stated that establishing data governance and internal data management are barriers that their organizations experience in creating a smooth audit experience. As organizations recognize the need to enhance their data governance practices, there are steps they can take to turn the challenge into an opportunity for improved audit quality and better information to manage businesses more effectively .
The Need for Data Governance and Structure
A lack of data inventory, along with a lack of structure across disparate systems, can create issues for organizations and the tools they use. Without an understanding of the most important business priorities driving a need for data quality – or knowing the data it has on hand – a company limits its visibility to information gaps and its ability to draw insights from that data. This subsequently makes risks assessments less effective and unreliable, giving an incomplete picture of risk across the organization. Conducting a data inventory is also an opportunity to begin the organization process, including identifying redundancies across different data repositories and checking for accuracy.
Accurate data is essential for audit quality and the use of advanced tools. Outputs and conclusions are based on the data they are drawn from, so any inaccuracies will be reflected in the results. But accuracy alone isn’t enough. Data scattered across multiple systems that sits in isolation is inaccessible to the tools that need it, meaning organizations must establish a process for data storage. That typically means leveraging cloud-based platforms that can be configured with the appropriate access levels for different users and systems. During this configuration, organizations must also consider the security implications of how data is accessed and who has access to it.
The way organizations save data is equally important. Data must be structured — meaning it is saved in a standardized, consistent format that is accessible to the people and systems that require it. Formatting data in this way enables analytics and extraction tools to function properly, helping to knock down a common barrier to an efficient audit experience.
Establishing a Strong Data Foundation
Moving from a place of unorganized, unstructured data to one of strong data governance lays a foundation for organizations to benefit in both the short and long term. In addition to the immediate benefits of enabling advanced tools and better audits, establishing data governance practices positions organizations for future regulatory mandates and emerging technology that will remain reliant on quality data.
There are several steps companies can take to implement and maintain data governance controls. These include:
- Implementing processes and policies for data standardization, access, and security
- Enacting a data infrastructure built within a cloud-based platform
- Enhancing data quality, which includes cleaning data regularly, checking for biases within the data, and creating a single source of truth
- Performing validity testing on the reliability of data inputs and outputs
Employing these practices addresses one of the key challenges in modern audits: compatibility with auditors’ tools. When data is structured and accessible, it allows systems and tools to interact with it properly, almost as though the data becomes a universal language. This subsequently offers a uniformity when extracting data, reducing the challenge of merging the data into auditors’ tools.
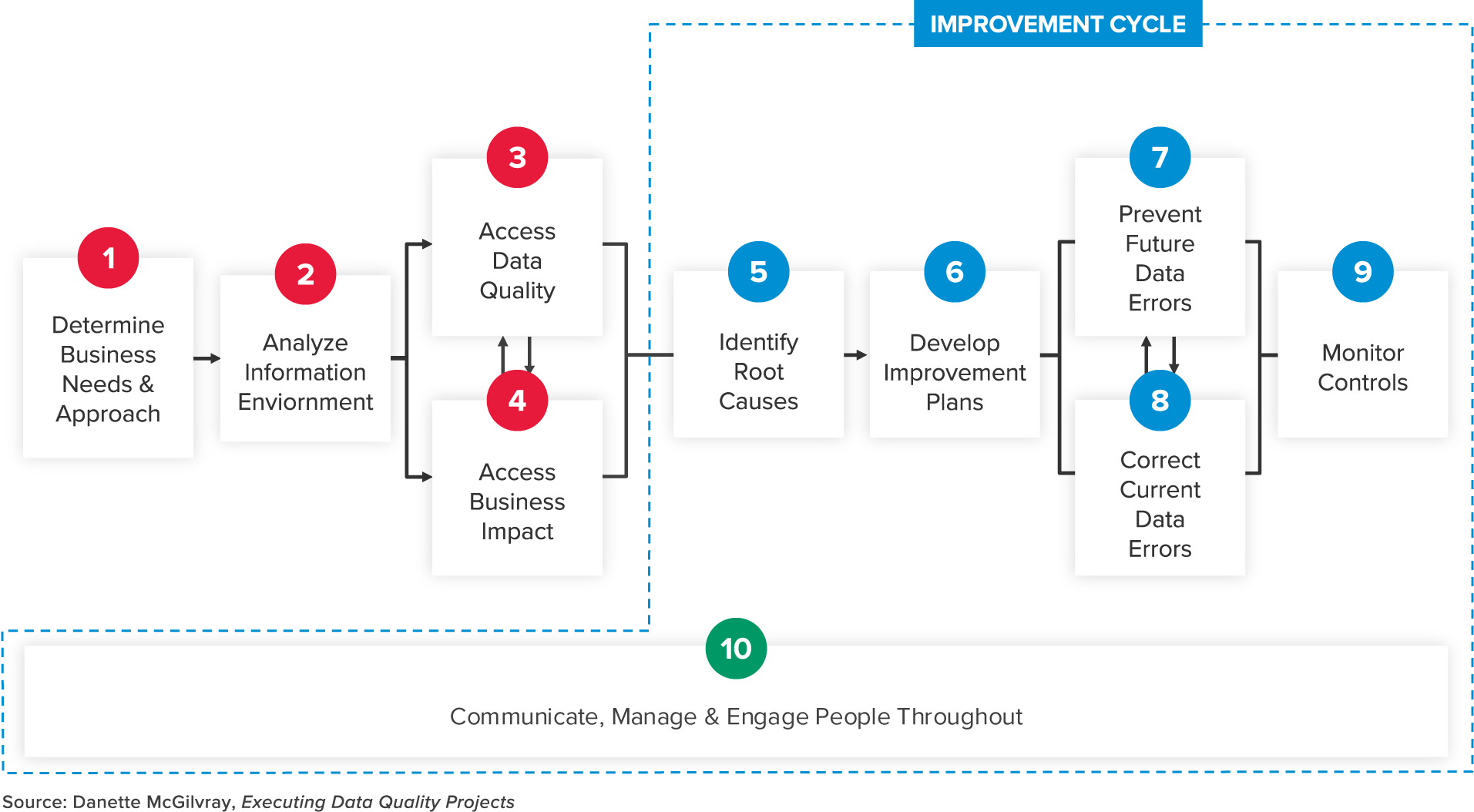
Establishing data structure is a significant undertaking for an organization, but it shouldn’t be seen as an insurmountable obstacle. Instead, it should be viewed as an opportunity to integrate effective data hygiene processes into standard operating procedures while establishing a precedent for future efforts. The 10 steps below are broken into two phases: the preliminary assessment and the improvement cycle. This can serve as a starting point for companies to begin their data structuring efforts and act as a guide along the way.
- Establish Business Need
- Perform Current State Assessment
- Evaluate Data Accuracy
- Assess Enterprise Effect
- Create Problem/Opportunity Statements
- Build Incremental Enhancement Plan
- Develop Data Controls
- Authenticate Data Accuracy
- Apply and Measure Data Performance Metrics
- Enable People, Processes, and Platforms
 zoom_in
zoom_inPurpose of the Data
Structuring data isn’t just for the audit and doesn’t need to be an overwhelming task for organizations. In fact, many companies acknowledge that it’s something they should already be doing as part of good data hygiene and overall best practices. A solid data foundation provides a platform that can help organizations conduct better risk assessments, enable AI-powered tools, and create a smooth audit experience.
Visit our Audit Innovation page to learn more.